John Cagney and Paul McBride examine the use of high-friction surfacing on Irish roads; outlining its cost, its effectiveness, and drawing attention to recent examples.
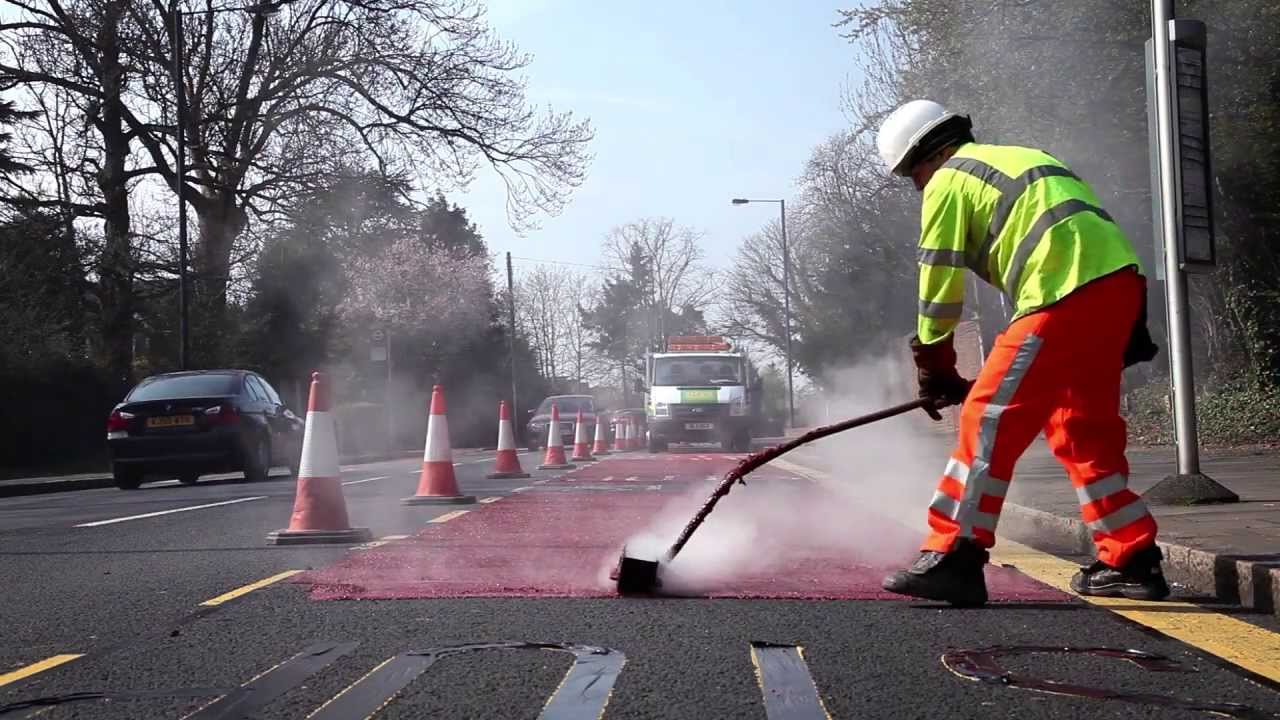
High Friction Surfacing (HFS), commonly termed Anti-skid, refers to a surface treatment approximately 3-5mm thick which provides enhanced surface skid resistance for drivers to brake under emergency conditions at hazardous locations. . Typical locations for HFS installation include approaches to roundabouts, pedestrian crossings, junctions, sites with steep gradients and dangerous bends.
HFS has a long history of proven use in saving lives by imparting the highest level of skid resistance onto a road surface and is available as hot applied or cold applied systems. Cold applied HFS systems are similar to surface dressing in that they involve the even application of a tough polymeric liquid binder onto the prepared road surface followed by the application of calcined bauxite aggregate. The hot applied systems involve the application of a hot pre-mixed material consisting of binder and calcined bauxite.

The concept was first investigated in the USA during the 1950s using epoxy resin binders and was first known as anti-skid surfacing. In the UK, the first evaluation trials were conducted in 1967 for the Greater London Council. The study over a period of 12 months demonstrated a 50% reduction in skid related accidents and casualties on roads treated with high friction surfacing. Numerous studies since have demonstrated HFS typically reduces accidents by 35%.
In Dublin, Northstone have recently completed over 3,500m2 at Chapelizod Bypass & Con Colbert Road including the junction with South Circular Road. The project involved the installation of 15 lane junction approaches of HFS plus some infill sections on SCR. Roadstone, who were Main Contractor to Dublin City Council (DCC), had resurfaced the carriageway in October 2015. Given the time of year HFS works had to be deferred and were completed in May 2016.
How does HFS work?
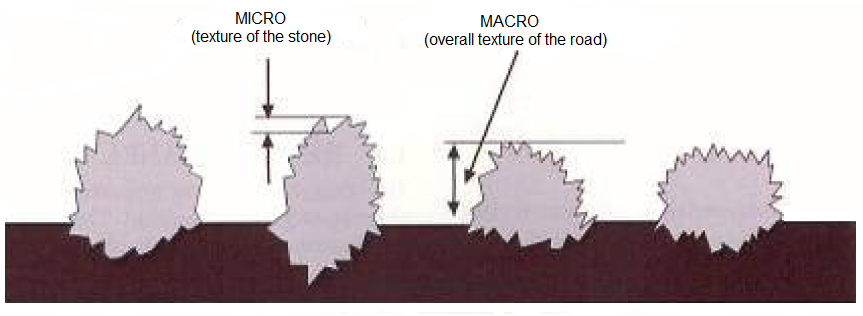
The high level of skid resistance is imparted by the calcined bauxite aggregate used in HFS systems. Calcined bauxite is a manufactured aggregate with exceptional resistance to abrasion caused by vehicle tyres combined with a very high resistance to polishing.
Calcined bauxite micro-texture results in reduced contact points with vehicle tyres creating high contact pressure points and improved hydraulic conductivity which are critical for high skid resistance.
When to use high friction surfacing
On sites where there is high risk of accidents resulting from collisions between vehicles or between vehicles and pedestrians – pedestrian crossings, junctions, roundabouts, etc.
Cost effectiveness
Though HFS is relatively high cost, a balanced budget allocation that accounts for accident investigation and prevention demonstrates returns on investment. Financially, there are major cost consequences for emergency services, local and national governments. Not to mention the immeasurable cost to the accident victims, their families and friends.
Which roads can be treated with high friction surfacing?
All classes of road, from single track, unclassified roads to high speed urban routes, trunk roads and motorways can and have been successfully treated with HFS.
Service Life
An ADEPT & RSTA study in 2011 concluded that HAPAS accredited Cold Applied HFS should last between 5 & 11 years with a service life (mid-point) of eight years. Additionally, in 2013 the BBA commenced a study on the performance of HFS. The study was initiated by a general drop in demand for HFS and a perception that HFS offered inferior durability and no longer provided value for money, compared to alternative high PSV surfacing. Published in December 2015 after assessing 272 HFS locations, the conclusion was that 95% of sites were performing after five years, with failed sites condemned due to poor substrate and/or installation workmanship. Conversely ‘High PSV Asphalt Surfacing’ has been indicated to be performing poorly, with TRL in 2014 experiencing marginal Scrim values within 12 months and returning to HFS at safety critical areas.
Recent Site follow-up assessments in Dublin indicate systems performing very well after 5 Yrs. The installed systems were HAPAS accredited Cold applied HFS systems incorporating calcined bauxite, installed by HAPAS accredited Operatives.
In 2008, Northstone installed HFS for Dublin City Council on Swords Road at Collins Avenue junction outbound and at Iveragh Road Junction inbound. As can be seen from these recent pictures, both locations have met their service life expectations and would appear to have several years of useful life remaining. It is quite possible that the HFS will only fail due to the failure of the underlying substrate.

Swords Road Collins Avenue Junction
High friction surfacing is an established, proven process for saving lives by imparting the highest level of skid resistance onto any road surface. HFS systems properly specified and installed on a well prepared substrate have been shown to provide the highest level of skid resistance over a 10 year service life. Despite its construction cost, the effectiveness of HFS at dramatically reducing skid related accidents should make it a top priority, as it is an extremely cost effective solution when compared to the value prevention by avoiding collision related fatalities.













